使用 Spring Cloud Contract
1. 在 Nexus 或 Artifactory 中使用存根的提供商合同测试
你可以查看“开发你的第一个春季云合同基于应用”链接,查看提供商合同测试中 Nexus 或 Artifactory 流程中的存根。
2. 在 Git 中使用存根的提供者合同测试
在这个流程中,我们会进行提供者合同测试(生产者对消费者如何使用他们的 API 一无所知)。这些存根会上传到单独的仓库(它们不会上传到 Artifactory 或 Nexus)。
2.1. 前提条件
$ tree .
└── META-INF
└── folder.with.group.id.as.its.name
└── folder-with-artifact-id
└── folder-with-version
├── contractA.groovy
├── contractB.yml
└── contractC.groovy2.2. 流动
流程看起来与《开发你的第一个春季云合约应用》中呈现的完全相同,
但存根存储实现是一个 git 仓库。
你可以了解更多关于如何搭建git仓库以及设置消费者端和生产端的内容 在文档的“作指南”页面。
2.3. 消费者设置
如果你想从git仓库里获取stub,而不是Nexus或Artifactory,你
需要使用git协议中 URL 的repositoryRootStub Runner的房产。
以下示例展示了如何设置:
@AutoConfigureStubRunner(
stubsMode = StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE,
repositoryRoot = "git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git",
ids = "com.example:artifact-id:0.0.1")
@Rule
public StubRunnerRule rule = new StubRunnerRule()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);
@RegisterExtension
public StubRunnerExtension stubRunnerExtension = new StubRunnerExtension()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);
2.4. 制作人设立
要把存根推送到 git 仓库,而不是 Nexus 或 Artifactory,你需要
使用git插件设置的URL中包含协议。另外你需要明确说明
插件是在构建过程结束时推送存根的。以下示例显示
如何在Maven和Gradle中实现:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<!-- Base class mappings etc. -->
<!-- We want to pick contracts from a Git repository -->
<contractsRepositoryUrl>git://git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git</contractsRepositoryUrl>
<!-- We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts -->
<contractDependency>
<groupId>${project.groupId}</groupId>
<artifactId>${project.artifactId}</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</contractDependency>
<!-- The contracts mode can't be classpath -->
<contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<!-- By default we will not push the stubs back to SCM,
you have to explicitly add it as a goal -->
<goal>pushStubsToScm</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>contracts {
// We want to pick contracts from a Git repository
contractDependency {
stringNotation = "${project.group}:${project.name}:${project.version}"
}
/*
We reuse the contract dependency section to set up the path
to the folder that contains the contract definitions. In our case the
path will be /groupId/artifactId/version/contracts
*/
contractRepository {
repositoryUrl = "git://git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git"
}
// The mode can't be classpath
contractsMode = "REMOTE"
// Base class mappings etc.
}
/*
In this scenario we want to publish stubs to SCM whenever
the `publish` task is run
*/
publish.dependsOn("publishStubsToScm")
你可以在文档的“如何做”部分了解更多关于如何搭建git仓库的内容。
3. 由生产者方签订的消费者驱动合同
参见《消费者驱动的逐步指南》 与生产者方合同(CDC)的合同,以查看消费者驱动的合同 合同则集中在生产方流动。
4. 基于外部仓库中的客户驱动合同
在这个流程中,我们进行消费者驱动的合同测试。合同定义如下 存储在一个独立的仓库中。
4.1. 前提条件
要使用基于消费者的合同和外部仓库中持有的合同,你需要搭建一个git仓库,满足以下功能:
-
包含每个生产者的所有合同定义。
-
可以把合同定义打包在 JAR 里。
-
对于每个契约生产者,包含一种方式(例如,
pom.xml)以安装存根 本地通过 Spring Cloud Contract 插件(SCC 插件)实现。
你还需要消费者代码,并且已经设置了 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner。 关于此类项目的示例,请参见此示例。 你还需要制作人代码,里面有Spring Cloud Contract,并配有插件。 关于此类项目的示例,请参见此示例。 存根存储是Nexus或Artifactory。
在高层次,流动如下:
-
消费者则从独立仓库中作合同定义。
-
一旦消费者完成工作,就会在消费者身上创建带有工作代码的分支 Side,并且会向存放合同定义的独立仓库发送拉取请求。
-
生产者接管了拉取请求到带有合同的独立仓库 定义并安装所有合同的JAR。
-
生产者从本地存储的 JAR 生成测试并写入缺失的 实现以使测试通过。
-
生产者的工作完成后,调用存储库的 合同定义被合并。
-
CI 工具构建包含合同定义的仓库,JAR 则用 合同定义上传到 Nexus 或 Artifactory,生产者可以合并其分支。
-
最后,消费者可以转为在线工作,从以下平台获取生产者的存根 远程位置,分支可以合并到主节点。
4.2. 消费者流
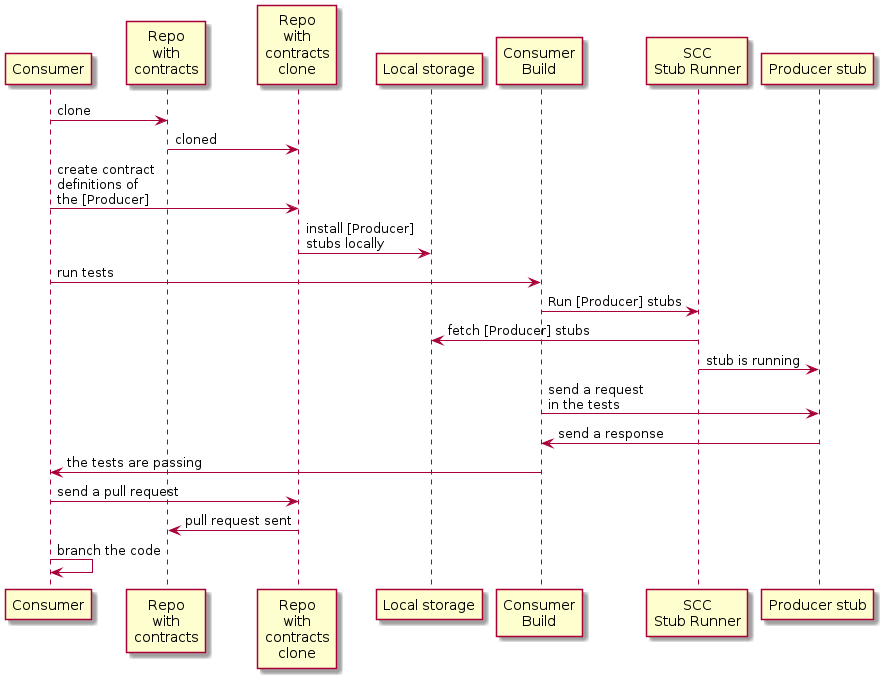
消费者:
-
写一个测试,发送请求给制作人。
由于没有服务器存在,测试失败了。
-
克隆存放合同定义的仓库。
-
将需求设置为文件夹下的合同,消费者名称作为生产者的子文件夹。
例如,对于一个名为
制作人以及一位名为消费者合同将存储在SRC/主/资源/合约/生产者/消费者/) -
一旦合同定义,就会将生产者存根安装到本地存储,如下示例所示:
$ cd src/main/resource/contracts/producer $ ./mvnw clean install -
在消费者测试中设置春季云合约(SCC)存根运行器,目的是:
-
从本地存储中获取生产者的存根。
-
在每个消费者的存根模式下工作(这支持了消费者驱动的合约模式)。
SCC短篇跑者:
-
拿制片人的存根。
-
运行内存内的 HTTP 服务器存根,包含生产者存根。 现在你的测试与HTTP服务器存根通信,测试通过。
-
向仓库创建拉取请求,定义合同,并包含生产者的新合同。
-
它分支你的消费者代码,直到制作团队合并他们的代码。
-
下图显示了消费者的流程:
4.3. 制作人流程
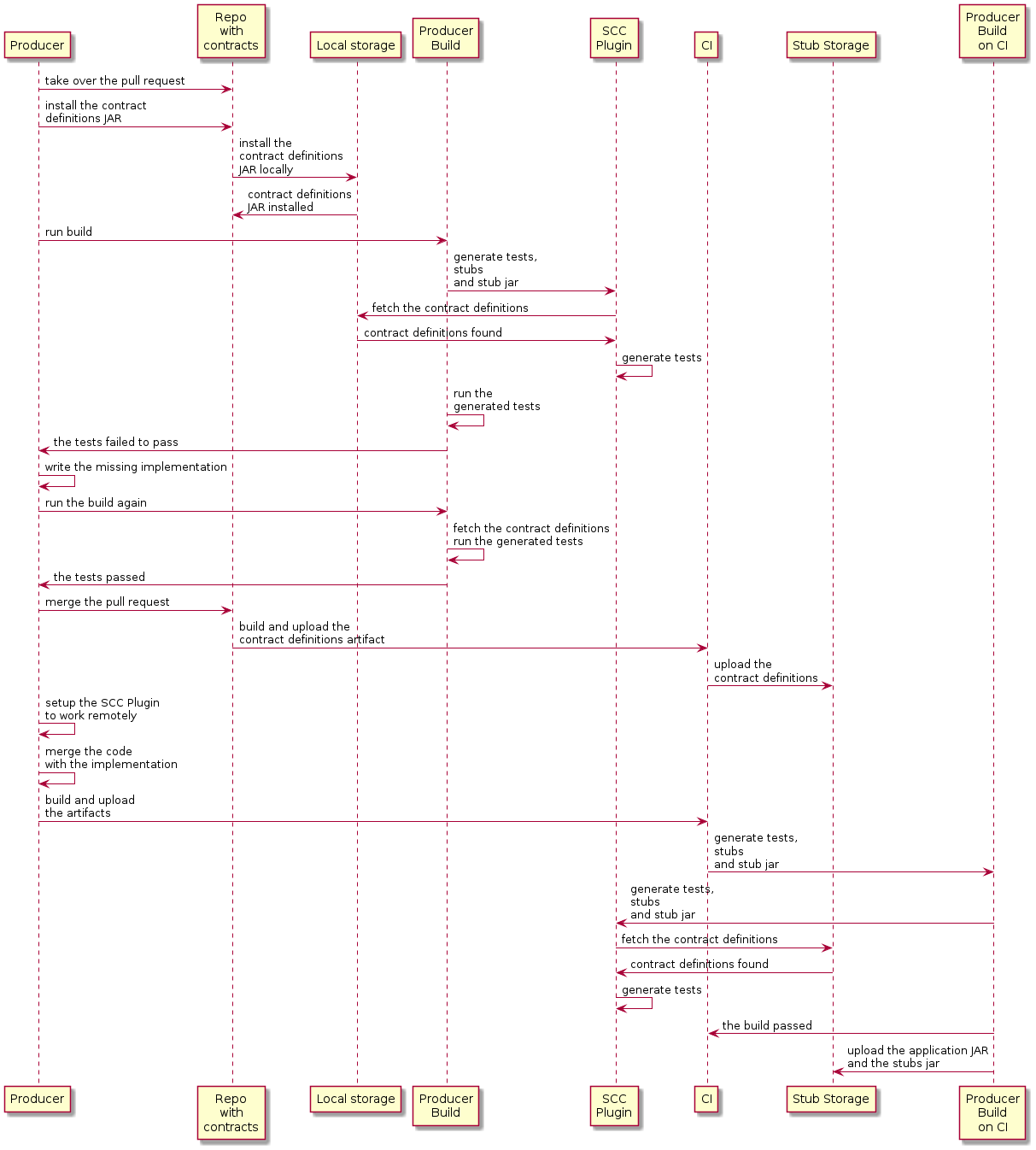
制片人:
-
它接管了带合同定义的仓库拉取请求。你可以的 从命令行中,具体如下
$ git checkout -b the_branch_with_pull_request master git pull https://github.com/user_id/project_name.git the_branch_with_pull_request -
安装合同定义,具体如下
$ ./mvnw clean install -
设置插件从JAR获取合同定义,而不是从那里获取
SRC/测试/资源/合同如下:梅文<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <configuration> <!-- We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates --> <contractDependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>beer-contracts</artifactId> </contractDependency> <!-- The JAR with contracts should be taken from Maven local --> <contractsMode>LOCAL</contractsMode> <!-- ... additional configuration --> </configuration> </plugin>格拉德勒contracts { // We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates // group id `com.example`, artifact id `beer-contracts`, LATEST version and NO classifier contractDependency { stringNotation = 'com.example:beer-contracts:+:' } // The JAR with contracts should be taken from Maven local contractsMode = "LOCAL" // Additional configuration } -
运行构建以生成测试和存根,具体如下:
梅文./mvnw clean install格拉德勒./gradlew clean build -
写出缺失的实现,使测试通过。
-
将拉取请求与合同定义合并到仓库,具体如下:
$ git commit -am "Finished the implementation to make the contract tests pass" $ git checkout master $ git merge --no-ff the_branch_with_pull_request $ git push origin masterCI系统会根据合同定义构建项目,并上传JAR,然后通过 合同定义为Nexus或Artifactory。
-
转为远程工作。
-
设置插件后,合同定义不再来自本地 但存储方式来自远程,具体如下:
梅文<plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version> <extensions>true</extensions> <configuration> <!-- We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates --> <contractDependency> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>beer-contracts</artifactId> </contractDependency> <!-- The JAR with contracts should be taken from a remote location --> <contractsMode>REMOTE</contractsMode> <!-- ... additional configuration --> </configuration> </plugin>格拉德勒contracts { // We want to use the JAR with contracts with the following coordinates // group id `com.example`, artifact id `beer-contracts`, LATEST version and NO classifier contractDependency { stringNotation = 'com.example:beer-contracts:+:' } // The JAR with contracts should be taken from a remote location contractsMode = "REMOTE" // Additional configuration } -
将生产者代码与新实现合并。
-
CI系统:
-
构建项目。
-
生成测试、存根和存根JAR。
-
将应用和存根一起上传到Nexus或Artifactory。
-
下图展示了生产者过程:
5. 以生产者端为主导的合同,推动启动
你可以阅读《消费者驱动合同逐步指南》(CDC),其中合同由生产者侧承担,了解消费者驱动合同与生产者侧合同流程。
存根存储实现是一个 git 仓库。我们在“Git中的提供商合同测试与存根”部分中描述了其设置。
你可以在以下内容中了解更多关于如何为消费者和生产者端搭建 git 仓库的信息 文档中的“作指南”部分。
6. 在Artifactory中为非Spring应用提供提供商合同测试,并带有存根
6.1. 心流
你可以阅读《开发你的第一个春云基于合同应用》,了解在Nexus或Artifactory中使用存根进行提供商合同测试的流程。
6.2. 建立消费者
对于消费者端,你可以用JUnit规则。这样你就不必开始春季语境。以下列表展示了此类规则(见JUnit4和JUnit 5);
@Rule
public StubRunnerRule rule = new StubRunnerRule()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);
@RegisterExtension
public StubRunnerExtension stubRunnerExtension = new StubRunnerExtension()
.downloadStub("com.example","artifact-id", "0.0.1")
.repoRoot("git://[email protected]:spring-cloud-samples/spring-cloud-contract-nodejs-contracts-git.git")
.stubsMode(StubRunnerProperties.StubsMode.REMOTE);
6.3. 设立制片人
默认情况下,Spring Cloud Contract 插件使用 Rest Assurance 的莫克麦克为
生成测试。由于非 Spring 应用不使用莫克麦克,你可以更改测试模式自明确发送真实请求给绑定在特定端口的应用程序。
在这个例子中,我们使用一个叫 Javalin 的框架来启动一个 非 Spring HTTP 服务器。
假设我们有以下应用:
package com.example.demo;
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DemoApplication().run(7000);
}
public Javalin start(int port) {
return Javalin.create().start(port);
}
public Javalin registerGet(Javalin app) {
return app.get("/", ctx -> ctx.result("Hello World"));
}
public Javalin run(int port) {
return registerGet(start(port));
}
}
给定该应用程序,我们可以设置插件使用明确模式(即 到
向真实端口发送请求,具体如下:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-contract-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-contract.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<baseClassForTests>com.example.demo.BaseClass</baseClassForTests>
<!-- This will setup the EXPLICIT mode for the tests -->
<testMode>EXPLICIT</testMode>
</configuration>
</plugin>contracts {
// This will setup the EXPLICIT mode for the tests
testMode = "EXPLICIT"
baseClassForTests = "com.example.demo.BaseClass"
}
基类可能类似于以下内容:
public class BaseClass {
Javalin app;
@Before
public void setup() {
// pick a random port
int port = SocketUtils.findAvailableTcpPort();
// start the application at a random port
this.app = start(port);
// tell Rest Assured where the started application is
RestAssured.baseURI = "http://localhost:" + port;
}
@After
public void close() {
// stop the server after each test
this.app.stop();
}
private Javalin start(int port) {
// reuse the production logic to start a server
return new DemoApplication().run(port);
}
}
采用这样的设置:
-
我们已经设置了 Spring Cloud Contract 插件来使用
明确发送实物的模式 请求而不是嘲笑的请求。 -
我们定义了一个基类:
-
每次测试都随机从一个端口启动HTTP服务器。
-
设置Rest Assured向该端口发送请求。
-
每次测试后关闭HTTP服务器。
-
7. 在非JVM世界中,Artifactory中的提供商合同测试与存根
在这个流程中,我们假设:
-
API Producer 和 API Consumer 是非 JVM 应用程序。
-
合同定义用YAML编写。
-
存根存储是人工存储或连接存储。
-
Spring Cloud Contract Docker (SCC Docker) 和 Spring Cloud Contract Stub Runner Docker (SCC Stub Runner Docker)镜像被使用。
你可以在这里了解更多关于如何使用 Docker 的 Spring Cloud Contract。
来,你可以 阅读一篇关于如何在多语种世界中使用春云合约的博客文章。
这里,你可以找到 这是一个NodeJS应用程序的示例,该应用既使用Spring Cloud Contract作为生产者,也是一个 消费者。
7.1. 制作流程
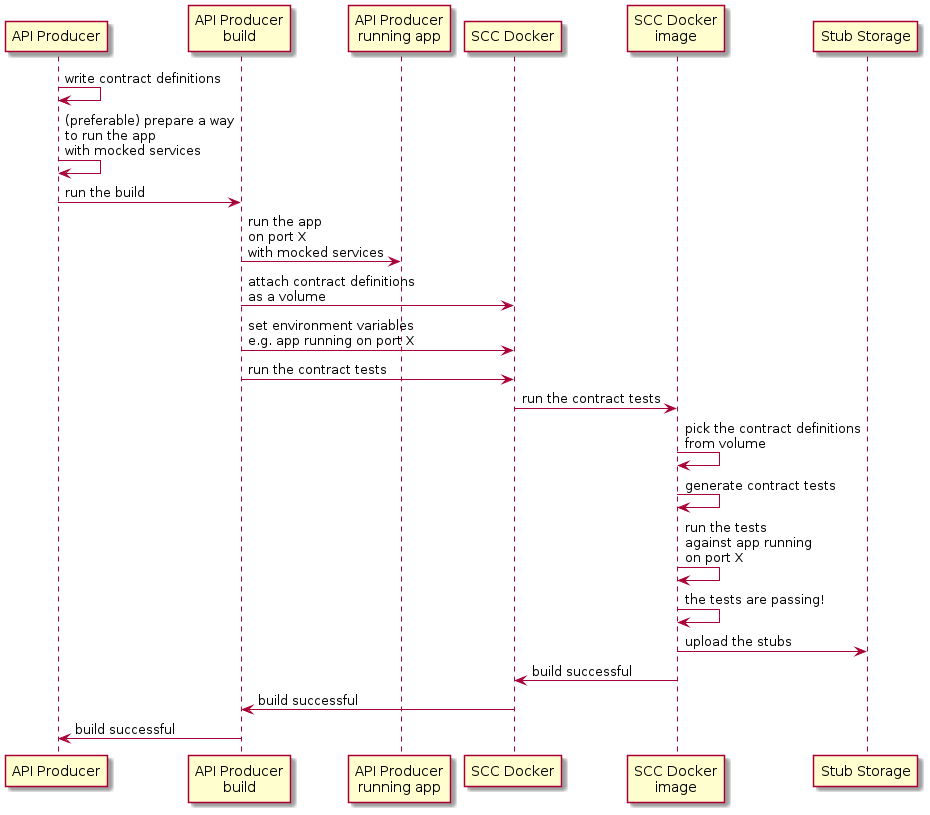
从高层次来看,制片人:
-
编写合同定义(例如,在YAML中)。
-
将构建工具设置为:
-
在某个端口上启动应用时,先用模拟服务。
如果无法模拟,你可以搭建基础设施并以有状态的方式定义测试。
-
运行 Spring Cloud Contract Docker 镜像,并将运行中的应用的移植作为环境变量传递。
-
SCC Docker 镜像: * 从附加卷生成测试。 * 对运行中的应用程序进行测试。
测试完成后,存根会上传到存根存储网站(如 Artifactory 或 Git)。
下图显示了生产者流程:
7.2. 消费者流动
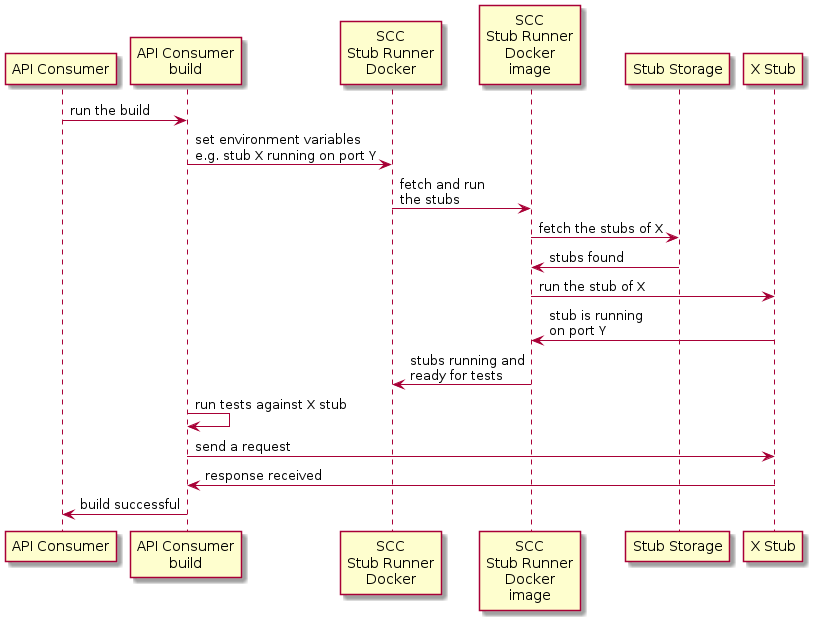
从高层次来看,消费者:
-
将构建工具设置为:
-
启动 Spring Cloud 合同 Stub Runner Docker 镜像并启动 stubs。
环境变量配置如下:
-
要去取的残头。
-
存储库的位置。
请注意:
-
要使用本地存储,也可以将其作为一个卷附加。
-
残管运行的端口需要暴露。
-
-
对运行中的存根进行应用测试。
下图显示了消费者的流程:
8. 在 Nexus 或 Artifactory 中使用 REST 文档和存根进行提供商合同测试
在这个流程中,我们不使用 Spring Cloud Contract 插件来生成测试和存根。我们编写 Spring RESTDocs,并自动生成存根。最后,我们设置构建,将存根打包并上传到存根存储网站——我们这里是Nexus或Artifactory。
8.1. 生产者流程
作为制片人,我们:
-
编写我们API的RESTDocs测试。
-
把Spring Cloud合同Stub Runner的起始角色加入我们的构建 (
春云启动合同存根跑者),具体如下:梅文<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>格拉德勒dependencies { testImplementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-contract-stub-runner' } dependencyManagement { imports { mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}" } } -
我们设置了构建工具来打包我们的存根,具体如下:
梅文<!-- pom.xml --> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId> <executions> <execution> <id>stub</id> <phase>prepare-package</phase> <goals> <goal>single</goal> </goals> <inherited>false</inherited> <configuration> <attach>true</attach> <descriptors> ${basedir}/src/assembly/stub.xml </descriptors> </configuration> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> <!-- src/assembly/stub.xml --> <assembly xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-assembly-plugin/assembly/1.1.3 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/assembly-1.1.3.xsd"> <id>stubs</id> <formats> <format>jar</format> </formats> <includeBaseDirectory>false</includeBaseDirectory> <fileSets> <fileSet> <directory>${project.build.directory}/generated-snippets/stubs</directory> <outputDirectory>META-INF/${project.groupId}/${project.artifactId}/${project.version}/mappings</outputDirectory> <includes> <include>**/*</include> </includes> </fileSet> </fileSets> </assembly>格拉德勒task stubsJar(type: Jar) { classifier = "stubs" into("META-INF/${project.group}/${project.name}/${project.version}/mappings") { include('**/*.*') from("${project.buildDir}/generated-snippets/stubs") } } // we need the tests to pass to build the stub jar stubsJar.dependsOn(test) bootJar.dependsOn(stubsJar)
现在,当我们运行测试时,存根会自动发布和打包。
下图显示了生产者流程:
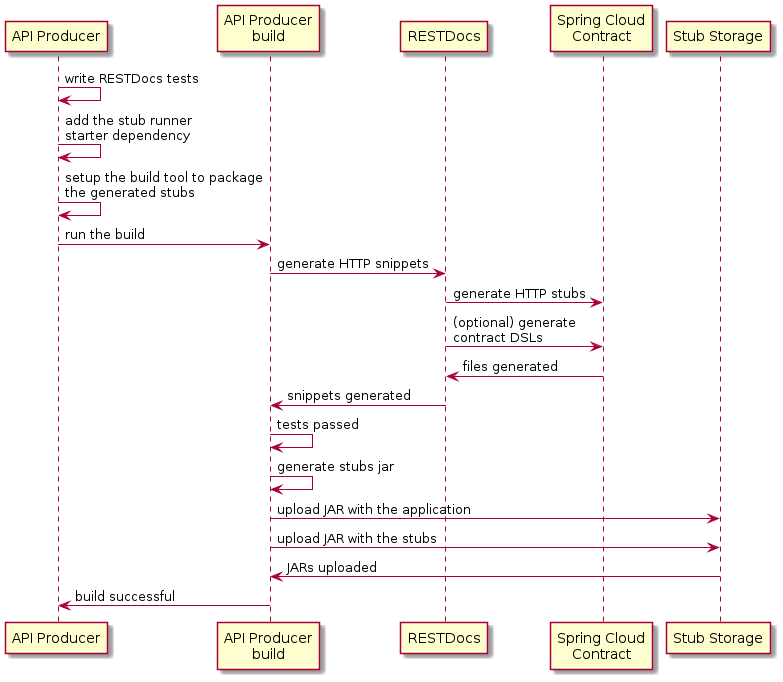
8.2. 消费者流
由于生成存根的工具不会影响消费者流程,你可以阅读《开发你的第一个春季云合同应用》,了解在Nexus或Artifactory中测试提供商合同中消费者端流程。
9. 接下来要读什么
你现在应该了解如何使用Spring Cloud Contract以及一些最佳实践 应该跟随。你现在可以继续学习Spring Cloud Contract的具体功能,或者你可以 跳过,阅读Spring Cloud Contract的高级功能。